Introduction to Anxiety:-
Anxiety is a common human emotion characterized by feelings of fear, worry, and unease.
Besides, It is a natural response to stress or danger and can be a helpful mechanism that prepares the body to face challenging situations.
However, when it becomes excessive, persistent, and interferes with daily life, it can develop into an anxiety disorder.
Management of Anxiety:-
Managing Anxiety involves a combination of strategies, which can be tailored to an individual’s needs. Some common approaches include:
1. Therapy:- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Exposure Therapy, and Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction are commonly used therapeutic techniques to help individuals manage anxiety by identifying and changing negative thought patterns.
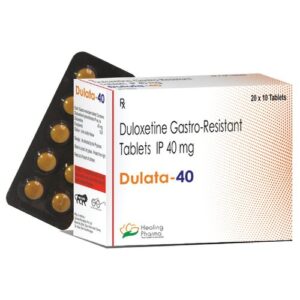
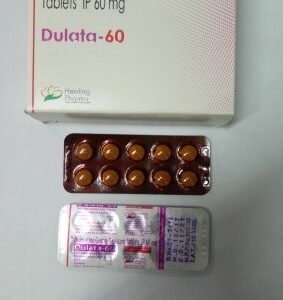
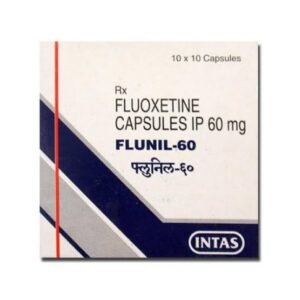
2. Medication:-Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications, such as Gabapentin, Duloxetine, Fluoxetine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), or benzodiazepines, may be prescribed by a medical professional for more severe cases of Anxiety.
3. Lifestyle Changes:- Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, practicing relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation), and getting enough sleep can help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
4. Support Systems:- Talking to friends, and family, or joining support groups can provide emotional comfort and understanding, reducing feelings of isolation.
Uses of Anxiety:-
While Anxiety is typically viewed as a negative emotion, it does have some evolutionary benefits. In its normal form, it can:
1. Enhance Alertness:- Anxiety triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, increasing alertness and preparing the individual to respond to potential threats.
2. Motivation:- It can motivate individuals to prepare for challenges or important events, encouraging them to perform at their best.
3. Problem-Solving:- It can prompt individuals to anticipate potential issues and plan for them, promoting better problem-solving skills.
Side Effects of Anxiety:-
Excessive or chronic it can have negative effects on both physical and mental well-being. Some side effects include:
1. Physical Symptoms:- Increased heart rate, muscle tension, headaches, stomach discomfort, and fatigue can result from prolonged it.
2. Cognitive Impact:- Anxiety can lead to difficulties in concentration, memory problems, racing thoughts, and impaired decision-making.
3. Emotional Distress:- It can cause intense emotional distress, including feelings of fear, panic, restlessness, irritability, and a sense of impending doom.
4. Social Isolation:- Individuals with it may withdraw from social interactions, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
5. Impact on Daily Life:- It can interfere with work, relationships, and daily activities, reducing the overall quality of life.
In conclusion, It is a complex emotion that serves both protective and detrimental roles.
While it can be beneficial in certain situations, chronic or it requires proper management and support to ensure a person’s overall well-being.
Although, If it becomes overwhelming, seeking professional help is essential to address its impact on mental and physical health.
Different Dosage:-
Gabapentin